Some collected tips and tricks for sendmail and related mail utilities. For more documentation, see the cf/README, sendmail/SECURITY, and doc/op/op.ps files under the sendmail source. Example permissions for sendmail 8.12 and up.
.forward
The ~/.forward file can be used to customize mail flow. Three different destination types may be used.
- Address
- Force local delivery
- Literal file
Remote email address to relay the mail to, such as user@example.net.
To force delivery to the local mailbox, precede the mailbox name (typically the username) with a backslash: \user.
To specify a literal file where mail should be deposited, use a fully qualified path: /home/user/archive/mailstore.
The above can be combined as comma separated values on a single line, or on multiple lines to split mail delivery to multiple destinations.
Disabling .forward
Disabling the .forward file makes sense where the mail setup is complicated or users are otherwise prone to mess things up by inserting procmail invocation rules from 1995 that make no sense with procmail as the local delivery agent. Additionally, the mail system will not have to parse the user details out of the system accounts and lookup the .forward, which can speed mail processing.
To disable forward file support, set an empty forward file search path in the sendmail.mc file, and rebuild sendmail.cf.
define(`confFORWARD_PATH', `')
Delaying Email
Outgoing email may be held by default by setting the DeliveryMode option to deferred. The queue will need to be run manually (or periodically from cron, or when a network connection is available from a script) to flush the queued messages. On a laptop that relays mail through a central server without running a local sendmail daemon, set something like following in submit.mc to hold mail by default.
FEATURE(`msp', `mail.example.org')
define(`confDELIVERY_MODE', `deferred')
Normally definitions do not follow the msp feature, but this is an exception to that rule.
For the main sendmail daemon, update the sendmail.mc.
define(`confDELIVERY_MODE', `deferred')
MAILER(`smtp')
Expect to see the following warning when rebuilding the configuration files.
$ sudo make config
WARNING: Antispam rules not available in deferred delivery mode.
WARNING: Antispam rules not available in deferred delivery mode.
Disable ident
The Identification Protocol (see [RFC 1413]) allows the user of a particular Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection to be queried. In the context of email, the Mail Transport Agent (MTA) such as Sendmail will send a ident connection back to the client to see which user on the sending system is sending mail. I recommend that ident lookups be disabled, as most systems will either not run an ident daemon or will have the port firewalled or otherwise blocked, thus requiring extra useless work by the mail server.
To disable ident support, set the confTO_IDENT timeout in the sendmail.mc file to zero, then rebuild sendmail.cf.
define(`confTO_IDENT', `0')
enhdnsbl
Enhanced version of dnsbl. Requires sendmail to be compiled with DNSMAP support. For instance, to support the Spamhaus Block List, use something like the following. Other services may do RBL lookups, such as Mail::SpamAssassin, so review the mail flow to ensure duplicate work is not being done.
FEATURE(`enhdnsbl', `sbl.spamhaus.org', ↵
`Mail from $&{client_addr} rejected see http://www.spamhaus.org/SBL', ↵
`t', `127.0.0.2.')
mailertable
The mailertable file can be used to direct mail for particular domains to specific hosts. To enable this feature, set the following in your sendmail.mc and rebuild sendmail.cf.
FEATURE(`mailertable')
The should result in a sendmail.cf that contains a Kmailertable line listing the path to the mailertable file plus some ruleset code.
$ grep ^Kmailertable /etc/mail/sendmail.cf
Kmailertable hash /etc/mail/mailertable
- Avoid Mail Exchange (MX) lookups for internal hosts.
- Target a specific remote server.
- Wildcard all hosts in domain into class {w}.
On mail proxy systems with lower (or the only) MX values than the eventual destination machine for the mail in question, use brackets around the target server to prevent MX lookups and "mail loops back to self" errors.
example.org esmtp:[mail.example.org]
.example.org esmtp:[mail.example.org]
special.example.org esmtp:[special.example.org]
The outgoing mail for a particular domain can be directed at a named server with the same syntax as above. A use for this is to route mail for a particular domain through a different server, for example when the domain example.net blocks mail from “dial-up” class subnets under the example.org domain, but does accept mail from the central mail server mail.example.org.
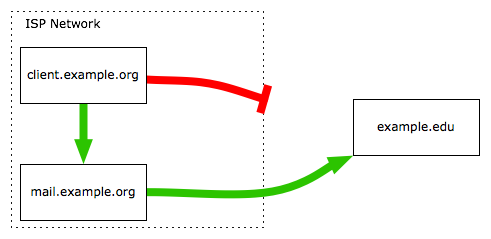
For complex mailertable setups, a default rule may be needed. The following changes need to be done on the client hosts under the example.org domain.
# default rule needed?
. esmtp:%1%0
# use central mail.example.org host to route example.net mail to
example.net esmtp:mail.example.org
.example.net esmtp:mail.example.org
A general solution to the above problem is to use the FallbackMXhost option, which can be used to add a specified mail server as the last option when attempting to send mail to a host. This may obviate the need to add additional mailertable entries for each problematic domain.
define(`confFALLBACK_MX', `mail.example.org')
By default, each hostname to be treated as local by sendmail must be listed in class {w}, usually via entries in the /etc/mail/local-host-names configuration files and subsequent sendmail restarts. This is not ideal for sites that want to accept all domain e-mail as local by default. To solve this problem, create the following mailertable entry.
.example.org local:
If certain hosts under the domain in question accept their own e-mail, add mailertable entries for each such host in question.
subhost.example.org esmtp:[subhost.example.org]
Move messages to slow queue
Tip on using qtool.pl and a cron job to move slow messages to a slow queue.
Spamtrap User
To trap all mail sent locally to a non-existent user, create a LUSER_RELAY definition in the sendmail.mc file. This could also be done for particular domains using a mailertable entry.
Using a trap-all user may seem like a good method to prevent spammers from determining what user accounts are on a system, but will also trap legitimate mail sent to an incorrect address (e.g. via a typo on the username). I would only user a trap-all on an entire domain dedicated to the purpose.
define(`LUSER_RELAY', ``local:user'')
Transport Layer Security (TLS) Tips
Sendmail can be built for TLS support, often in conjunction with SMTP AUTH to provide remote relaying services. The access map allows control over how or when TLS is negotiated with clients. See also notes on configuring CipherList support in sendmail, to alter what algorithms are used by the server.
Incompatible Clients
Incoming mail servers that accept mail from the Internet may need TLS support disabled, as there could be interoperability problems with poorly implemented TLS services in other MTA.
To disable all advertisement of TLS services, add the following to the access map file.
Srv_Features: S
Older, slower systems may want to disable STARTTLS, as the cryptographic computations may delay mail significantly.
Another option would be to enable TLS on the lowest MX for a domain, and have a higher MX without TLS that uninteroperable systems would presumably fail over to. The same could be done for outgoing systems, where the primary outgoing systems attempt TLS, but not the FallbackMXhost host.
Incompatible Servers
In addition to senders having problems negotiating with your server, your systems may also have problems connecting with certain remote servers. The logfiles should show entries similar to the following for the problematic server.
sm-mta[1234]: ruleset=tls_server, arg1=SOFTWARE, relay=mail.example.com, ↵
reject=403 4.7.0 TLS handshake failed.
The solution is to add access map entries that disable TLS with the host (or domain, for multiple remote servers with problems) in question.
Try_TLS:mail.example.com NO
Loopback
TLS should be disabled over the localhost interface, as there is almost no need for such mail to be encrypted.
Srv_Features:localhost.localdomain S
SMTP AUTH Interaction
Servers that use STARTTLS to tunnel client connections will likely need to disable client certificate checks, as most clients will not have a certificate to present. Mail User Agents (MUA) such as Netscape Messenger may also prompt the user for a certificate, compounding the problem.
To disable all client certificate checks, set the following in the access map.
Srv_Features: V
On the other hand, a server that allows relaying by certificate will need to have client certificate checks enabled to properly verify the client.
Procmail
In sendmail, a good way to enable procmail is to configure it as the local mailer, which avoids having to setup any ~/.forward rules to pass mail to procmail.
dnl use this in place of MAILER(`local')
MAILER(`procmail')
Depending on the system, procmail may need to have the suid root or sgid mode bits set (or removed for security) so that local mail can be written as the user in question.
